Hearing Evaluation, Hearing Devices & Earlens
Basic & Comprehensive Audiological Evaluations
Patients who suffer from hearing loss, or other hearing-related conditions, may benefit from audiologic testing. Comprehensive diagnostic exams can determine the causes, severity of, and best treatment for hearing-related conditions. Audiologic tests are usually performed after other diagnostic tests have indicated the presence of a possible hearing problem.
Audiogram
This hearing test uses sounds of specific frequencies and intensity levels to determine what a person can hear in each ear. The sounds are heard through headphones, and the patient is asked to identify each sound and the ear in which it was heard. The sounds become fainter and fainter, ultimately determining the lowest level at which a patient can hear. An audiogram may also include speech in the form of two-syllable words to determine how well a patient can comprehend what is being heard.
Custom: Swim Molds, Hearing Protection, Musician’s Plugs
Ear swim molds will keep ears clean and dry while swimming, almost necessary for pediatric patients with ear tubes, especially during the summer. Hearing protection will safeguard your hearing from loud noises at work or during some hobbies such school marching band, woodworking and yard work.
Visual Reinforcement Audiometry
A modified version of the diagnostic audiogram, visual reinforcment audiometry allows for testing of younger children who otherwise would not understand the test instructions. The child is conditioned to look at an animated toy on either side of their head when sound is presented on that side. When conditioned, the sound may be presented alone, without animation of the toy. If the child continues to look towards the toy, we can determine that the sound was heard.
Tympanometry
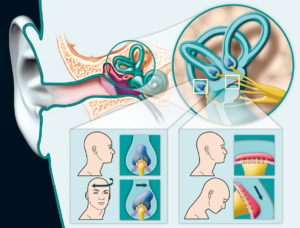
This form of testing examines and diagnoses problems in the middle ear by varying air pressure in the ear canal to see how the ear responds. A probe is inserted into the ear to change the air pressure, produce a tone and measure the responses. The patient may not speak, move or swallow during the test because doing so can affect ear pressure. Tympanometry measures the functionality of the eardrum (tympanic membrane). Abnormal findings may be the result of fluid in the middle ear, a perforated ear drum or impacted ear wax.
Otoacoustic Emissions Testing (OAE)
Otoacoustic emissions testing (OAE) measures response to a sound from the cochlea, or the inner part of the ear. The hair cells inside the cochlea vibrate in response to sound. These vibrations produce a nearly inaudible sound that echoes back into the middle ear.
This test is performed by inserting a microphone and two speakers into the ear to emit a sound and then record the response signal. The test is often performed on children when hearing loss is a possibility. An OAE may also be conducted as part of the newborn hearing screening process. Absent or very soft response signals may be a sign of hearing loss, fluid behind the ears or damage to the cochlea.Select a Topic Below:
To learn more about our services contact our office directly 850-889-4550 .